Gastroparesis refers to a delay in emptying stomach contents. Symptoms often include feeling full after eating a meal, or even a small amount of food, as well as nausea, vomiting, bloating or abdominal pain. The causes of gastroparesis may include diabetes mellitus, complications after surgery, kidney disease, certain medications, thyroid disorders, cancer, among others.
The following tips are intended to reduce symptoms and help maintain adequate nutrition.
|
Mealtime
|
||
|
Foods
|
|
|
Fluids
- Stay hydrated. Most adults need 6-10 cups of water per day. Sip slowly throughout the day.
- Drink fluids with meals, however; be sure not to fill up on liquids
- Avoid carbonated beverages as they can cause bloating
Other
- Avoid alcohol as it can affect stomach emptying
- Foods that are acidic, spicy, or contain caffeine or mint may increase acid reflux
- Keep blood sugars under control if you have diabetes
- Keep a food diary to track your intake and find foods that are best tolerated
- Exercise may increase stomach emptying and reduce symptoms. Walking after meals is suggested.
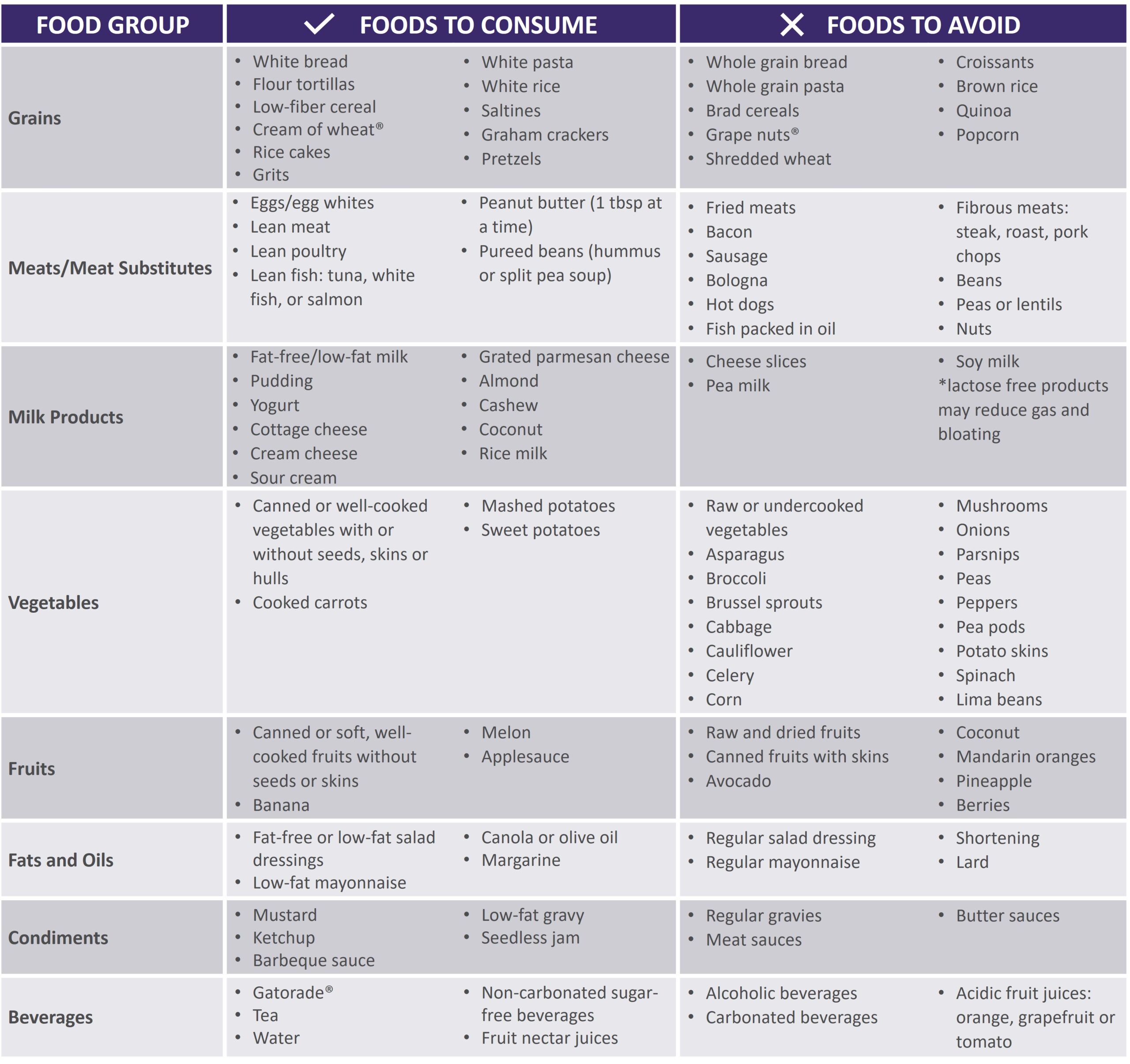
See below for help in choosing more optimal foods from each food group:
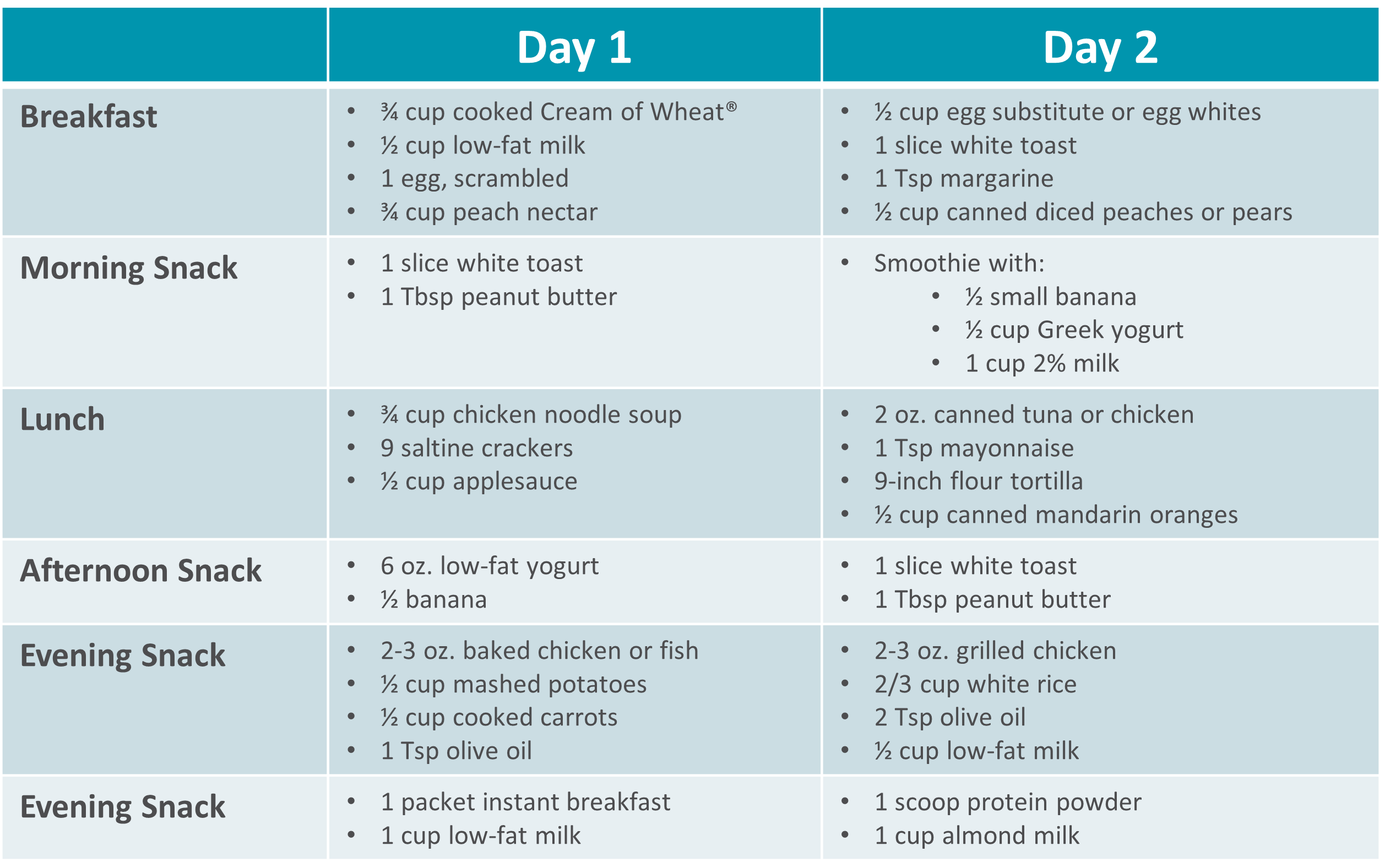
Gastroparesis Sample Menus
Please visit Restore+ to learn more about the nutrition support services offered by Option Care Health.
*This material is for informational purposes only. It does not replace the advice or counsel of a healthcare professional. Please consult with your Registered Dietitian for more detailed, individualized information.

